Evaluate 5 X3 2 7 When X
arrobajuarez
Oct 29, 2025 · 7 min read
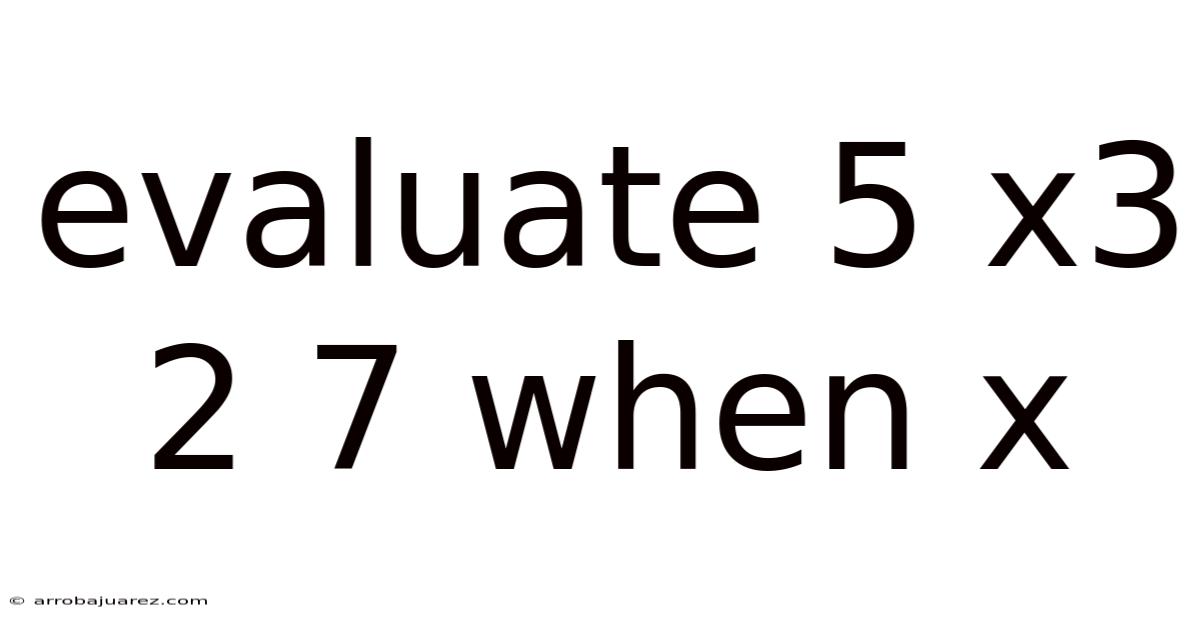
Table of Contents
Let's delve into the evaluation of the algebraic expression 5x³ - 27 when x = 2. This process involves substituting the variable x with its given value, 2, and then performing the arithmetic operations according to the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS). Understanding this evaluation is fundamental to grasping algebraic concepts and solving various mathematical problems.
Step-by-Step Evaluation
To accurately evaluate the expression, we need to follow a systematic approach:
- Substitution: Replace every instance of the variable x in the expression with the value 2. This transforms the algebraic expression into a numerical expression.
- Exponentiation: Calculate any exponents present in the expression. In this case, we have x³ which becomes 2³.
- Multiplication: Perform all multiplication operations in the expression. Here, we have 5 multiplied by the result of 2³.
- Subtraction: Finally, perform any subtraction operations. In our case, we subtract 27 from the result of the multiplication.
Let's execute each step in detail:
Step 1: Substitution
The original expression is 5x³ - 27. Replacing x with 2, we get:
5(2)³ - 27
Step 2: Exponentiation
We need to calculate 2³. This means 2 * 2 * 2, which equals 8. Substituting this back into the expression, we have:
5(8) - 27
Step 3: Multiplication
Now, we perform the multiplication: 5 * 8 = 40. The expression becomes:
40 - 27
Step 4: Subtraction
Finally, we subtract: 40 - 27 = 13
Therefore, the value of the expression 5x³ - 27 when x = 2 is 13.
A Deeper Dive into the Order of Operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS)
The acronym PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction) or BODMAS (Brackets, Orders, Division and Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction) provides a crucial framework for simplifying and evaluating mathematical expressions. It ensures that calculations are performed in a standardized order, leading to a consistent and correct result. Let's explore each component of this order:
- P/B (Parentheses/Brackets): Operations inside parentheses or brackets are always performed first. This allows us to group terms and dictate the order of calculations within the expression.
- E/O (Exponents/Orders): Next, we evaluate exponents (powers) or orders (roots). This involves raising a number to a certain power or finding the root of a number.
- MD (Multiplication and Division): Multiplication and division are performed from left to right. These operations are of equal precedence, so the order in which they appear in the expression dictates the order of evaluation.
- AS (Addition and Subtraction): Finally, addition and subtraction are performed from left to right, similar to multiplication and division.
Failing to adhere to the order of operations can lead to incorrect results. For instance, in the expression 5 + 2 * 3, if we perform addition before multiplication, we would get (5 + 2) * 3 = 7 * 3 = 21, which is incorrect. The correct answer, following PEMDAS/BODMAS, is 5 + (2 * 3) = 5 + 6 = 11.
Importance of Variables and Algebraic Expressions
Understanding how to evaluate expressions with variables is fundamental to algebra and its applications. Here's why:
- Representing Unknowns: Variables, like x in our example, are used to represent unknown quantities. This allows us to create equations and inequalities to model real-world situations.
- Generalization: Algebraic expressions provide a way to generalize mathematical relationships. Instead of dealing with specific numbers, we can use variables to represent a range of values.
- Problem Solving: Evaluating expressions is a key skill in solving algebraic problems. It allows us to determine the value of an expression for specific values of the variables, helping us to find solutions to equations and inequalities.
- Functions: Algebraic expressions form the basis of functions. A function is a relationship between an input (the variable) and an output (the value of the expression). Understanding how to evaluate expressions is crucial for understanding functions and their properties.
- Modeling Reality: Many real-world phenomena can be modeled using algebraic expressions. For example, the distance traveled by an object moving at a constant speed can be represented by the expression d = rt, where d is the distance, r is the rate (speed), and t is the time.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When evaluating algebraic expressions, several common mistakes can lead to incorrect answers. Being aware of these pitfalls can help you avoid them:
- Incorrect Order of Operations: As discussed earlier, failing to follow PEMDAS/BODMAS is a frequent source of errors. Make sure to perform operations in the correct order.
- Sign Errors: Pay close attention to the signs of numbers and variables. A negative sign can easily be missed, leading to an incorrect result. For example, -x when x = -2 becomes -(-2) = 2.
- Incorrect Substitution: Double-check that you have correctly substituted the value of the variable into the expression. Errors in substitution can propagate through the entire calculation.
- Arithmetic Errors: Even simple arithmetic errors can derail the evaluation. Take your time and double-check your calculations to minimize these mistakes. Using a calculator can also help, but make sure you understand the underlying concepts.
- Forgetting Parentheses: When substituting a negative value for a variable, use parentheses to avoid sign errors. For example, if x = -3, then x² should be written as (-3)², not -3². The former is 9, while the latter is -9.
- Distributing Negatives Incorrectly: When an expression involves subtracting a quantity within parentheses, remember to distribute the negative sign to all terms inside the parentheses. For example, 5 - (x + 2) becomes 5 - x - 2.
Examples with Varying Complexity
Let's explore more examples to solidify your understanding of evaluating algebraic expressions, including those with more complex operations and multiple variables:
Example 1: Evaluating with Multiple Variables
Evaluate the expression 2a² + 3b - c when a = 3, b = -1, and c = 5.
- Substitution: 2(3)² + 3(-1) - 5
- Exponentiation: 2(9) + 3(-1) - 5
- Multiplication: 18 - 3 - 5
- Subtraction: 18 - 8 = 10
Therefore, the value of the expression is 10.
Example 2: Evaluating with Fractions
Evaluate the expression (4x + 2) / ( x - 1) when x = 3.
- Substitution: (4(3) + 2) / (3 - 1)
- Multiplication: (12 + 2) / (3 - 1)
- Addition/Subtraction (within parentheses): 14 / 2
- Division: 7
Therefore, the value of the expression is 7.
Example 3: Evaluating with Negative Exponents
Evaluate the expression x⁻² + 2x when x = 2. Remember that x⁻² = 1/x².
- Substitution: 2⁻² + 2(2)
- Negative Exponent: (1/2²) + 2(2)
- Exponentiation: (1/4) + 2(2)
- Multiplication: (1/4) + 4
- Addition: 0.25 + 4 = 4.25 or 17/4
Therefore, the value of the expression is 4.25 or 17/4.
Example 4: Evaluating with Absolute Value
Evaluate the expression |3x - 5| when x = -1. Remember that absolute value returns the non-negative value of an expression.
- Substitution: |3(-1) - 5|
- Multiplication: |-3 - 5|
- Subtraction: |-8|
- Absolute Value: 8
Therefore, the value of the expression is 8.
Example 5: A More Complex Example
Evaluate the expression √(x² + 7) - (2x - 1)³ when x = 3.
- Substitution: √(3² + 7) - (2(3) - 1)³
- Exponentiation (inside square root and parentheses): √(9 + 7) - (6 - 1)³
- Addition/Subtraction (inside square root and parentheses): √16 - (5)³
- Square Root: 4 - (5)³
- Exponentiation: 4 - 125
- Subtraction: -121
Therefore, the value of the expression is -121.
Real-World Applications
Evaluating algebraic expressions has wide-ranging applications in various fields:
- Physics: Calculating the velocity, acceleration, or energy of an object using formulas involving variables.
- Engineering: Determining the stress, strain, or flow rate in a structure or system using equations with variables.
- Finance: Calculating interest, loan payments, or investment returns using formulas with variables.
- Computer Science: Evaluating algorithms and data structures using expressions with variables.
- Economics: Modeling economic trends and predicting market behavior using equations with variables.
- Everyday Life: Calculating the total cost of items at a store, determining the distance traveled on a road trip, or adjusting recipes based on the number of servings needed.
Conclusion
Mastering the evaluation of algebraic expressions is a fundamental skill in mathematics and has broad practical applications. By understanding the order of operations, avoiding common mistakes, and practicing with various examples, you can confidently tackle algebraic problems and apply these skills to real-world scenarios. The ability to manipulate and evaluate expressions empowers you to solve problems, model relationships, and make informed decisions in various fields of study and everyday life. Remember to always double-check your work and pay close attention to details to ensure accuracy in your calculations. Continue practicing and exploring more complex expressions to further enhance your understanding and proficiency.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Evaluate 5 X3 2 7 When X . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.