Sales Less Sales Discounts Less Sales Returns And Allowances Equals
arrobajuarez
Nov 03, 2025 · 11 min read
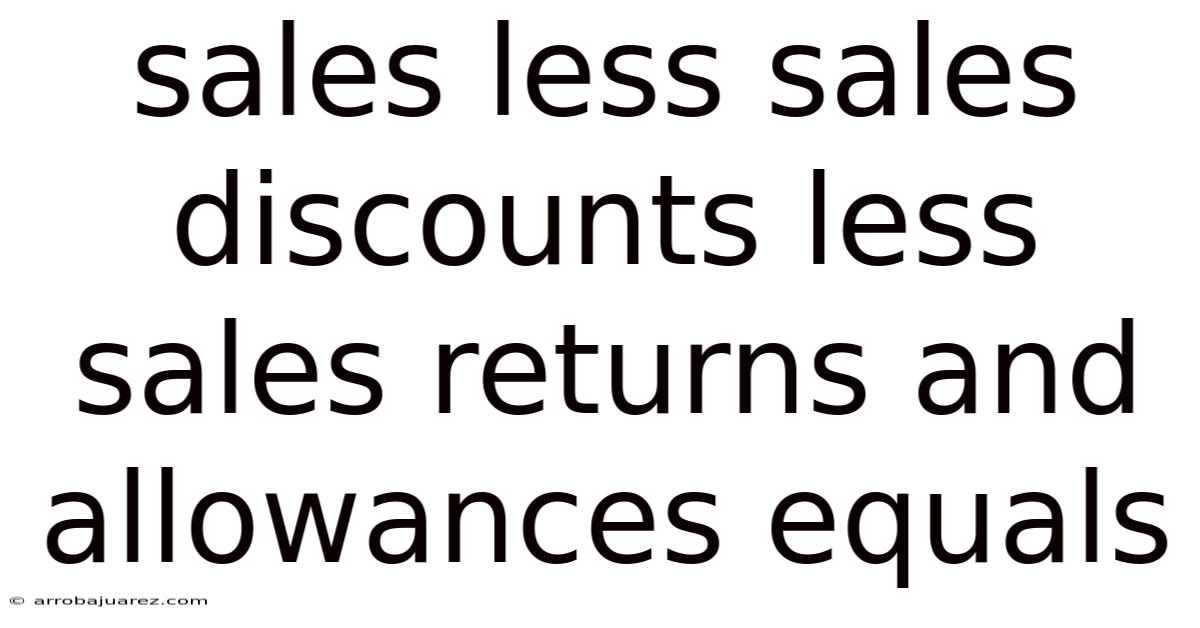
Table of Contents
In the world of business, understanding financial statements is crucial for making informed decisions and assessing the health of a company. One fundamental aspect of financial reporting is the accurate calculation of net sales, which provides a clearer picture of a company's revenue after accounting for various deductions. The formula "Sales less Sales Discounts less Sales Returns and Allowances equals Net Sales" is a cornerstone of this calculation. This article delves into the intricacies of each component of this formula, explaining their individual significance and how they collectively contribute to determining a company's net sales figure. By understanding these concepts, businesses and stakeholders can gain valuable insights into a company's financial performance and overall profitability.
Understanding Gross Sales: The Starting Point
Gross sales represent the total revenue generated from the sale of goods or services during a specific period, without any deductions. It is the initial figure that reflects the overall sales activity of a company. Gross sales serve as the foundation for calculating net sales and provide a broad overview of a company's revenue-generating capabilities.
What Constitutes Gross Sales?
Gross sales encompass all revenue earned from the primary business activities of a company. This includes:
- Cash Sales: Revenue received immediately at the time of sale.
- Credit Sales: Revenue earned from sales made on credit, where payment is deferred to a later date.
- Service Revenue: Revenue generated from providing services to customers.
- Sales of Products: Revenue earned from the sale of tangible goods.
Importance of Tracking Gross Sales
Tracking gross sales is essential for several reasons:
- Revenue Assessment: It provides a clear indication of the total revenue generated by a company before any deductions.
- Performance Evaluation: Gross sales can be compared over different periods to assess the growth and performance of a company.
- Financial Analysis: It serves as a starting point for calculating net sales and other key financial metrics.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Gross sales data is crucial for budgeting and forecasting future revenue.
Sales Discounts: Incentivizing Prompt Payment
Sales discounts are reductions in the selling price offered to customers as an incentive for early payment. These discounts are typically expressed as a percentage of the sale price and are designed to encourage customers to pay their invoices promptly. Sales discounts benefit both the buyer and the seller by improving cash flow and reducing the risk of bad debts.
How Sales Discounts Work
Sales discounts are usually offered under specific terms, such as "2/10, n/30," which means that the customer will receive a 2% discount if they pay within 10 days, otherwise the full amount is due within 30 days. The terms can vary depending on the industry, the relationship between the buyer and seller, and the prevailing market conditions.
Accounting for Sales Discounts
When a sales discount is offered and utilized, the company must account for it properly in its financial records. The journal entry typically involves debiting the sales discounts account (a contra-revenue account) and crediting the accounts receivable account. This reflects the reduction in revenue due to the discount.
For example, suppose a company makes a sale of $1,000 with terms 2/10, n/30. If the customer pays within 10 days, they will receive a 2% discount, which is $20. The journal entry would be:
- Debit: Sales Discounts $20
- Credit: Accounts Receivable $20
Benefits of Offering Sales Discounts
Offering sales discounts provides several benefits:
- Improved Cash Flow: Encourages customers to pay promptly, improving the company's cash flow.
- Reduced Risk of Bad Debts: Lower risk of customers defaulting on payments due to the incentive for early payment.
- Enhanced Customer Relationships: Demonstrates a willingness to work with customers, fostering better relationships.
- Competitive Advantage: Can attract more customers by offering favorable payment terms.
Sales Returns and Allowances: Addressing Customer Dissatisfaction
Sales returns and allowances represent reductions in revenue due to returned goods or price concessions made to customers for defective or unsatisfactory products. These adjustments are essential for maintaining customer satisfaction and accurately reflecting the actual revenue earned by a company.
Understanding Sales Returns
Sales returns occur when customers return merchandise for various reasons, such as defects, damages, or dissatisfaction with the product. When a product is returned, the company must reverse the original sale by reducing revenue and reinstating inventory.
Understanding Sales Allowances
Sales allowances are price reductions granted to customers who agree to keep defective or unsatisfactory merchandise instead of returning it. This is often a more cost-effective solution for the company, as it avoids the costs associated with processing returns and restocking inventory.
Accounting for Sales Returns and Allowances
Accounting for sales returns and allowances involves adjusting the revenue and related accounts to reflect the reduction in sales. The journal entry typically involves debiting the sales returns and allowances account (a contra-revenue account) and crediting either cash (for cash refunds) or accounts receivable (for credit sales).
For example, suppose a customer returns a product worth $100 due to a defect. The journal entry would be:
- Debit: Sales Returns and Allowances $100
- Credit: Cash/Accounts Receivable $100
Importance of Tracking Sales Returns and Allowances
Tracking sales returns and allowances is crucial for several reasons:
- Accurate Revenue Reporting: Provides a more accurate representation of net sales by accounting for reductions due to returns and allowances.
- Customer Satisfaction: Addresses customer dissatisfaction and helps maintain positive relationships.
- Quality Control: Highlights potential issues with product quality or customer service, allowing the company to take corrective actions.
- Inventory Management: Facilitates proper inventory management by accounting for returned goods.
Calculating Net Sales: The Complete Formula
Net sales represent the actual revenue a company earns after deducting sales discounts, sales returns, and allowances from gross sales. It is a more accurate measure of a company's revenue-generating capabilities than gross sales because it accounts for various reductions.
The Formula
The formula for calculating net sales is:
Net Sales = Gross Sales - Sales Discounts - Sales Returns and Allowances
Example Calculation
Suppose a company has the following data:
- Gross Sales: $500,000
- Sales Discounts: $10,000
- Sales Returns and Allowances: $5,000
Using the formula, the net sales would be:
Net Sales = $500,000 - $10,000 - $5,000 = $485,000
Significance of Net Sales
Net sales is a critical metric for assessing a company's financial performance and profitability. It provides a clearer picture of the actual revenue earned by a company after accounting for various deductions.
- Profitability Analysis: Net sales is used to calculate gross profit and net profit, which are key indicators of a company's profitability.
- Performance Evaluation: Comparing net sales over different periods can reveal trends in a company's revenue-generating capabilities.
- Financial Ratios: Net sales is used in various financial ratios, such as the net profit margin, which measures the percentage of net sales that is profit.
Practical Examples and Case Studies
To further illustrate the concepts discussed, let's examine some practical examples and case studies.
Example 1: Retail Company
A retail company, "Fashion Forward," had the following sales data for the month of June:
- Gross Sales: $250,000
- Sales Discounts: $5,000
- Sales Returns: $2,000
- Sales Allowances: $1,000
First, we calculate the total sales returns and allowances:
Total Sales Returns and Allowances = Sales Returns + Sales Allowances Total Sales Returns and Allowances = $2,000 + $1,000 = $3,000
Next, we use the formula to calculate net sales:
Net Sales = Gross Sales - Sales Discounts - Sales Returns and Allowances Net Sales = $250,000 - $5,000 - $3,000 = $242,000
In this example, Fashion Forward's net sales for June were $242,000, reflecting the actual revenue earned after accounting for discounts, returns, and allowances.
Example 2: Manufacturing Company
A manufacturing company, "Tech Solutions," had the following sales data for the year:
- Gross Sales: $1,000,000
- Sales Discounts: $20,000
- Sales Returns: $10,000
- Sales Allowances: $5,000
First, we calculate the total sales returns and allowances:
Total Sales Returns and Allowances = Sales Returns + Sales Allowances Total Sales Returns and Allowances = $10,000 + $5,000 = $15,000
Next, we use the formula to calculate net sales:
Net Sales = Gross Sales - Sales Discounts - Sales Returns and Allowances Net Sales = $1,000,000 - $20,000 - $15,000 = $965,000
Tech Solutions' net sales for the year were $965,000, providing a more accurate representation of the company's revenue.
Case Study: Amazon
Amazon, the global e-commerce giant, reports both gross sales and net sales in its financial statements. Gross sales include the total value of products and services sold, while net sales represent the actual revenue recognized after deducting discounts, returns, and allowances.
Amazon's net sales are a critical metric for assessing its financial performance and profitability. By analyzing the difference between gross sales and net sales, investors and analysts can gain insights into the company's pricing strategies, customer satisfaction, and overall operational efficiency.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
While the calculation of net sales is straightforward, several common pitfalls can lead to inaccuracies. Understanding these pitfalls and implementing proper controls can help ensure accurate financial reporting.
1. Incorrectly Classifying Discounts
One common mistake is incorrectly classifying discounts as sales discounts when they should be classified as marketing expenses or promotional allowances. Sales discounts are specifically related to early payment incentives, while other types of discounts should be accounted for differently.
How to Avoid: Clearly define the criteria for sales discounts and ensure that all discounts are properly documented and classified.
2. Failing to Account for Returns and Allowances
Another pitfall is failing to accurately track and account for sales returns and allowances. This can result in an overstatement of revenue and an inaccurate representation of a company's financial performance.
How to Avoid: Implement a robust system for tracking sales returns and allowances, including proper documentation and approval processes.
3. Using Incorrect Data
Using incorrect or outdated data can also lead to errors in the calculation of net sales. It is essential to ensure that all sales data is accurate and up-to-date.
How to Avoid: Implement data validation procedures and regularly reconcile sales data with other financial records.
4. Not Following GAAP
Failure to follow Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) can result in inaccurate financial reporting. GAAP provides guidelines for accounting for sales discounts, returns, and allowances, and it is essential to adhere to these principles.
How to Avoid: Ensure that all accounting staff are properly trained in GAAP and that financial statements are prepared in accordance with these principles.
Best Practices for Managing Sales Discounts, Returns, and Allowances
To effectively manage sales discounts, returns, and allowances, companies should implement the following best practices:
- Establish Clear Policies: Develop clear policies and procedures for offering sales discounts, processing returns, and granting allowances.
- Implement Strong Controls: Implement strong internal controls to ensure that all discounts, returns, and allowances are properly documented and approved.
- Track and Analyze Data: Track and analyze data on sales discounts, returns, and allowances to identify trends and potential issues.
- Provide Training: Provide training to sales and customer service staff on how to properly handle discounts, returns, and allowances.
- Regularly Review Policies: Regularly review and update policies and procedures to ensure they remain effective and aligned with business objectives.
The Role of Technology in Managing Sales Data
Technology plays a crucial role in managing sales data and ensuring the accurate calculation of net sales. Accounting software, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems can automate many of the processes involved in tracking sales discounts, returns, and allowances.
Accounting Software
Accounting software such as QuickBooks, Xero, and SAP Business One can automatically calculate net sales based on the data entered. These systems provide tools for tracking sales discounts, returns, and allowances and generating financial reports.
CRM Systems
CRM systems such as Salesforce and Microsoft Dynamics 365 can help manage customer interactions and track sales data. These systems can provide valuable insights into customer behavior and help identify potential issues with product quality or customer service.
ERP Systems
ERP systems such as SAP S/4HANA and Oracle ERP Cloud integrate all aspects of a business, including sales, accounting, and inventory management. These systems can provide a comprehensive view of sales data and help ensure the accurate calculation of net sales.
Conclusion
Understanding the formula "Sales less Sales Discounts less Sales Returns and Allowances equals Net Sales" is essential for accurately assessing a company's financial performance and profitability. By understanding the individual components of this formula and implementing best practices for managing sales data, businesses can gain valuable insights into their revenue-generating capabilities and make informed decisions. Proper tracking and management of sales discounts, returns, and allowances not only lead to more accurate financial reporting but also contribute to improved customer satisfaction and overall operational efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, leveraging accounting software, CRM systems, and ERP systems will further enhance the ability of companies to manage sales data effectively and ensure the accurate calculation of net sales.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sales Less Sales Discounts Less Sales Returns And Allowances Equals . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.