Usage Patterns Are A Variable Used In Blank______ Segmentation.
arrobajuarez
Nov 27, 2025 · 9 min read
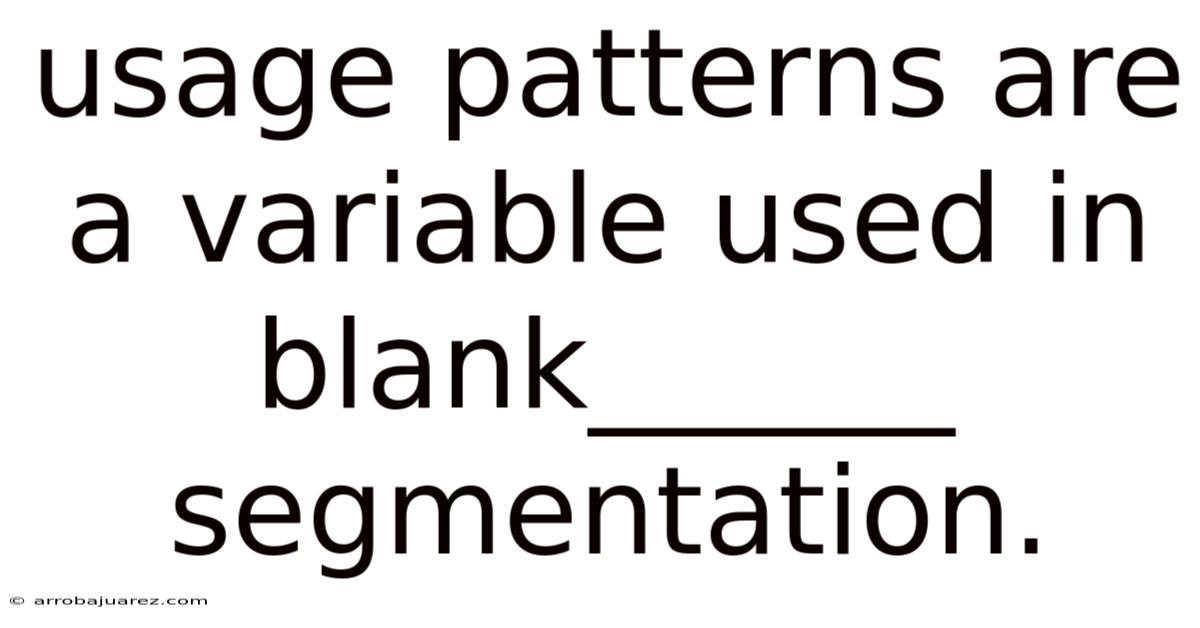
Table of Contents
Usage patterns are a variable used in behavioral segmentation, a crucial aspect of modern marketing strategies. Understanding how customers interact with products or services, including frequency of use, occasion, and loyalty status, allows businesses to tailor their marketing efforts for maximum impact. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the nuances of behavioral segmentation, particularly focusing on usage patterns and their application in creating targeted marketing campaigns.
Understanding Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation is a marketing strategy that divides a customer base into smaller groups based on their behaviors. These behaviors can include:
- Purchasing habits: What customers buy, how often they buy, and how much they spend.
- Usage: How customers use a product or service.
- Occasions: When customers make purchases or use products/services.
- Benefits sought: What customers are looking for in a product or service.
- Customer loyalty: How loyal customers are to a brand.
Unlike demographic or geographic segmentation, which focus on who the customer is or where they are, behavioral segmentation focuses on what the customer does. This allows for more personalized and effective marketing strategies.
The Significance of Usage Patterns
Usage patterns refer to how frequently and in what way customers interact with a product or service. Analyzing these patterns provides valuable insights into customer needs, preferences, and the value they derive from the offering. Here's why usage patterns are vital in behavioral segmentation:
-
Identifying Heavy Users: These customers are the most frequent users of a product or service and often contribute a significant portion of revenue. Understanding their needs and preferences is crucial for retention and loyalty programs.
-
Recognizing Light Users: These customers use the product or service infrequently. Understanding their reasons for light usage can help businesses identify barriers and develop strategies to increase engagement.
-
Spotting Non-Users: These are potential customers who are not currently using the product or service. Analyzing why they are not using it can reveal opportunities for targeted marketing and product improvements.
-
Understanding Usage Frequency: Knowing how often customers use a product or service helps businesses tailor their marketing messages and product offerings to match their consumption habits.
-
Identifying Usage Occasions: Understanding when customers use a product or service allows businesses to create targeted campaigns around specific events, holidays, or seasons.
Types of Usage Patterns
Usage patterns can be categorized in several ways, providing a multi-dimensional view of customer behavior. Here are some common types:
- Frequency of Use: This refers to how often a customer uses a product or service. It can be categorized as:
- Heavy Users: Use the product or service very frequently (e.g., daily or multiple times a day).
- Medium Users: Use the product or service moderately (e.g., weekly or a few times a month).
- Light Users: Use the product or service infrequently (e.g., monthly or less).
- Occasion of Use: This refers to when a customer uses a product or service, which can be:
- Regular Occasions: Use during routine events or activities (e.g., morning coffee).
- Special Occasions: Use during specific events or celebrations (e.g., champagne for anniversaries).
- Seasonal Occasions: Use during particular seasons or holidays (e.g., winter coats).
- Usage Rate: This refers to the amount of product or service a customer consumes within a given time period.
- High-Volume Users: Consume large quantities of the product or service.
- Low-Volume Users: Consume small quantities of the product or service.
- User Status: This refers to whether a customer is a:
- Non-User: Has never used the product or service.
- Prospect: Potential customer who is considering using the product or service.
- First-Time User: Recently started using the product or service.
- Regular User: Uses the product or service consistently.
- Defector: Former customer who has stopped using the product or service.
- Loyalty Status: This refers to how loyal a customer is to a brand, categorized as:
- Loyal Customers: Consistently purchase from the same brand.
- Switchers: Frequently switch between brands.
- Potential Loyals: Show signs of becoming loyal but are not yet fully committed.
Implementing Usage Pattern Segmentation: A Step-by-Step Guide
To effectively implement usage pattern segmentation, follow these steps:
-
Data Collection: Gather data on customer usage patterns. This can be done through various methods, including:
- Transaction data: Records of customer purchases, including date, time, product, and quantity.
- Website analytics: Data on how customers interact with a website, including pages visited, time spent on each page, and actions taken.
- Mobile app analytics: Data on how customers use a mobile app, including features used, frequency of use, and time spent on the app.
- Customer surveys: Surveys to gather information about customer preferences, behaviors, and satisfaction levels.
- CRM systems: Customer Relationship Management systems to track customer interactions and behaviors.
-
Data Analysis: Analyze the collected data to identify patterns and trends in customer usage. This may involve:
- Statistical analysis: Using statistical techniques to identify significant differences in usage patterns among different customer groups.
- Data mining: Using data mining techniques to discover hidden patterns and relationships in the data.
- Customer profiling: Creating detailed profiles of different customer segments based on their usage patterns.
-
Segmentation: Divide the customer base into distinct segments based on their usage patterns. This might involve:
- Clustering: Grouping customers with similar usage patterns into the same segment.
- Decision trees: Using decision trees to create rules for assigning customers to different segments based on their usage patterns.
-
Targeted Marketing: Develop targeted marketing strategies for each segment. This involves:
- Personalized messaging: Crafting marketing messages that resonate with the specific needs and preferences of each segment.
- Customized offers: Creating special offers and promotions tailored to each segment.
- Channel optimization: Selecting the most effective marketing channels for reaching each segment.
-
Evaluation and Refinement: Continuously evaluate the effectiveness of the segmentation strategy and make adjustments as needed. This includes:
- Tracking key metrics: Monitoring metrics such as customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, and customer retention rate.
- A/B testing: Experimenting with different marketing messages and offers to see what works best for each segment.
- Feedback collection: Gathering feedback from customers to understand their needs and preferences better.
Examples of Usage Pattern Segmentation in Action
Here are some examples of how businesses use usage pattern segmentation:
- Netflix: Netflix uses viewing history to recommend shows and movies to users. Heavy users of a particular genre might receive more recommendations for that genre, while light users might receive broader suggestions to encourage more viewing.
- Starbucks: Starbucks uses its rewards program to track purchase frequency and preferences. Frequent buyers might receive personalized offers for their favorite drinks, while infrequent buyers might receive incentives to visit more often.
- Amazon: Amazon uses purchase history to recommend products to customers. Heavy purchasers of books might receive recommendations for new releases, while light purchasers might receive recommendations for popular items in other categories.
- Software Companies: Software companies often segment users based on feature usage. Heavy users of advanced features might be offered training or support, while light users might receive tutorials or simplified interfaces to encourage more comprehensive usage.
- Mobile Gaming Apps: Mobile game developers analyze play frequency and duration. Heavy players might receive exclusive content or challenges, while infrequent players might get reminders or simpler tasks to keep them engaged.
Advantages of Usage Pattern Segmentation
There are several advantages to using usage pattern segmentation:
- Improved Customer Targeting: By understanding how customers use products or services, businesses can create more relevant and effective marketing campaigns.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: By providing personalized experiences, businesses can foster stronger relationships with their customers and increase loyalty.
- Enhanced Product Development: By analyzing usage patterns, businesses can identify opportunities to improve their products and services to better meet customer needs.
- Optimized Marketing Spend: By targeting marketing efforts to the most receptive segments, businesses can maximize the return on their marketing investment.
- Better Resource Allocation: Understanding which customer segments are most valuable allows businesses to allocate resources more efficiently.
Challenges of Usage Pattern Segmentation
Despite its many advantages, usage pattern segmentation also presents some challenges:
- Data Collection and Management: Collecting and managing the data needed for usage pattern segmentation can be complex and time-consuming.
- Privacy Concerns: Collecting and using customer data raises privacy concerns, and businesses must ensure they comply with all relevant regulations.
- Dynamic Nature of Usage Patterns: Customer usage patterns can change over time, requiring businesses to continuously monitor and update their segmentation strategies.
- Over-Segmentation: Dividing the customer base into too many small segments can make it difficult to develop and execute effective marketing campaigns.
- Interpretation of Data: Accurately interpreting usage data and translating it into actionable insights requires expertise and analytical skills.
Ethical Considerations
When implementing usage pattern segmentation, it's essential to consider ethical implications. Transparency and respect for customer privacy are paramount. Here are key considerations:
- Transparency: Clearly communicate data collection practices to customers. Explain how their usage data will be used and provide options for opting out.
- Data Security: Implement robust security measures to protect customer data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Fairness: Ensure that segmentation strategies do not discriminate against any particular group of customers.
- Data Minimization: Collect only the data that is necessary for the intended purpose. Avoid collecting excessive or irrelevant information.
- Customer Control: Give customers control over their data and the ability to access, modify, or delete it.
The Future of Usage Pattern Segmentation
The future of usage pattern segmentation is bright, driven by advancements in technology and data analytics. Here are some trends to watch:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI and machine learning algorithms will play an increasingly important role in analyzing usage data and identifying patterns.
- Real-Time Segmentation: Real-time data analysis will enable businesses to segment customers based on their current behavior and deliver personalized experiences in the moment.
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics will allow businesses to anticipate future customer behavior and proactively tailor their marketing efforts.
- Integration with IoT Devices: The Internet of Things (IoT) will provide new sources of data on customer usage patterns, enabling more granular and personalized segmentation.
- Enhanced Privacy Measures: Growing concerns about data privacy will drive the development of new technologies and regulations to protect customer data.
Conclusion
Usage patterns are a powerful variable in behavioral segmentation, enabling businesses to gain deep insights into how customers interact with their products and services. By understanding usage frequency, occasion, rate, user status, and loyalty, businesses can create targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with their customers, increase loyalty, and drive revenue growth. While there are challenges associated with data collection, privacy, and the dynamic nature of usage patterns, the benefits of implementing usage pattern segmentation far outweigh the risks. As technology continues to evolve, the future of usage pattern segmentation will be shaped by AI, real-time analytics, and enhanced privacy measures, providing businesses with even more opportunities to connect with their customers in meaningful ways.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Are Identical In Structure To Centrioles
Nov 27, 2025
-
What Is The Denotation Of A Word
Nov 27, 2025
-
Which Class Of Nutrients Does Not Contain Carbon
Nov 27, 2025
-
Find The Perimeter And Area Of The Polygon Shown Below
Nov 27, 2025
-
Put The Steps Of Dna Replication In The Correct Order
Nov 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Usage Patterns Are A Variable Used In Blank______ Segmentation. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.